|
|
|
|
|
Deodorization and sterilization
of fouled cutting oil by ozonization
| System flow of ozonization |
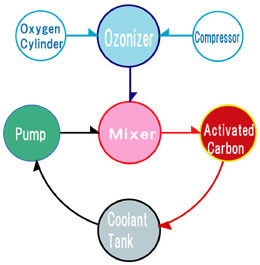 |
|
The unit prevents cuting oil from fouling at a low cost by circulating it in the specified mixing tank
with a built-in ozone generator where anaerobic bacteria are sterilized. |
| |
You can set it up easily by connecting the cutting oil tank with the
ozonization unit. |
| Installation is recommended with a new oil, however, the unit works well
even with a fouled oil and removes its rotten smell. |
| No waste is generated out of the unit because of its chemical decomposition
mechanism. |
|
| |
 |
 |
Oxygen |
 |
Ozon |
 |
Clean Cutting Oil |
 |
Cutting Oil |
|
|
| |
|
| Example of bacteria sterilization |
|
 |
|
 |
|
Total number of bacteria in cutting oil can be checked by a bacteria checker. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Photographs show the oil samples using oxygen.) |
|
before ozonization |
|
after ozonization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Example of deodorization |
|
 |
|
 |
|
Hydrogen sulfide and mercaptan, sources of the foul odor, are decreased by ozonization and those chemicals can be checked by a detector tube. |
|
|
| (Photographs show the detector tubes for mercaptan.) |
|
|
|
|
before ozonization |
|
after ozonization |
|
|